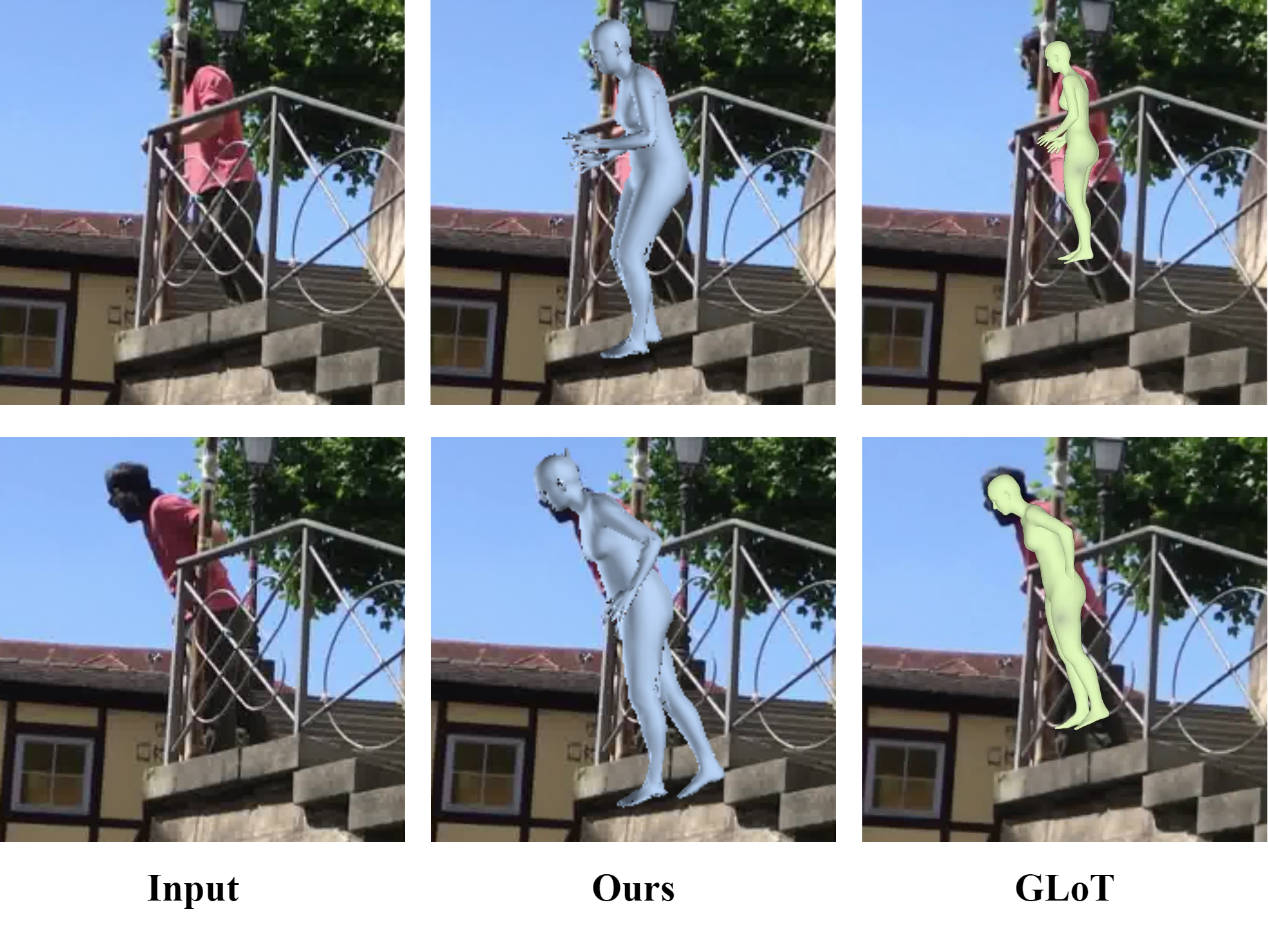
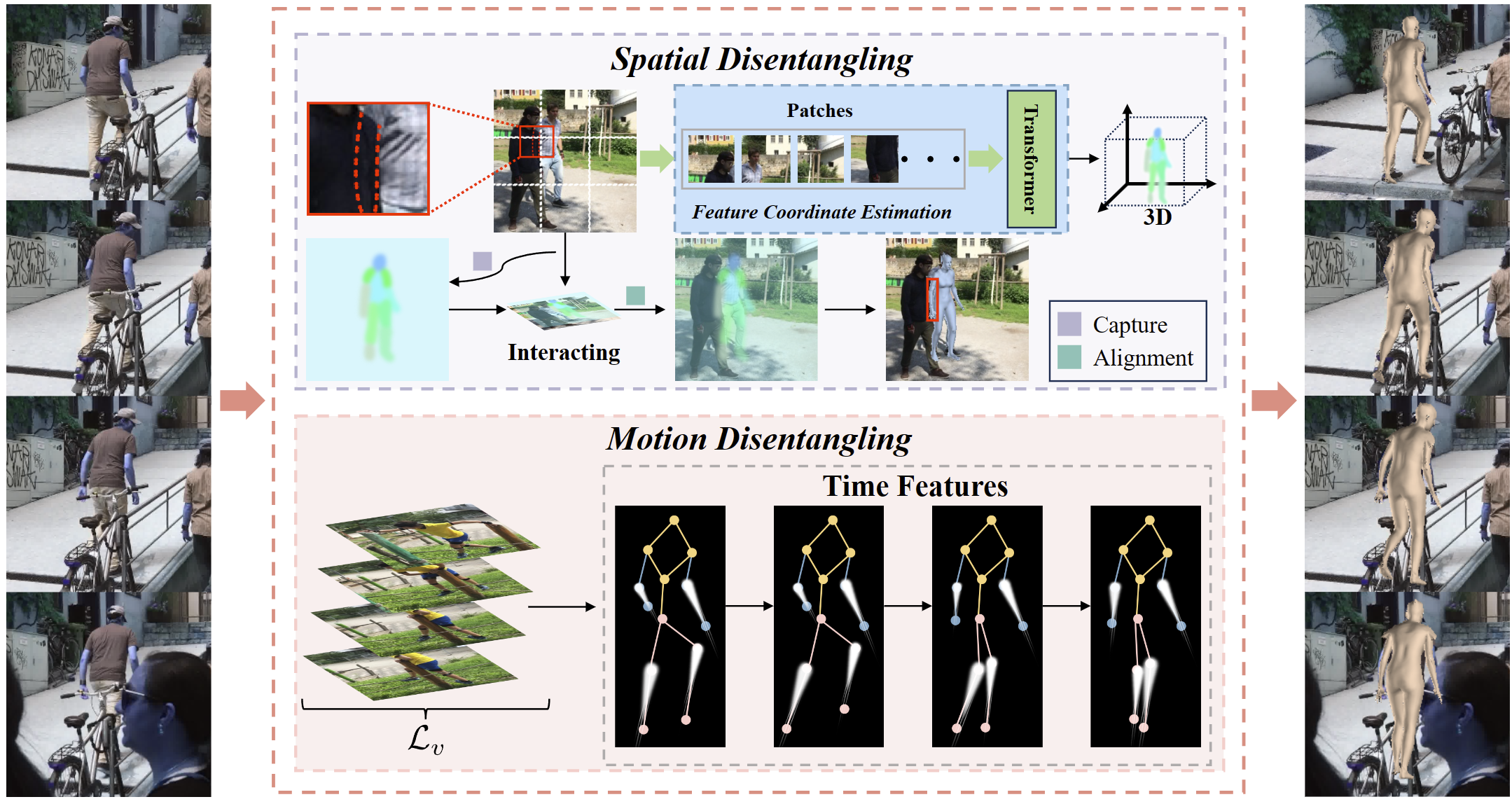
Reconstructing 3D human bodies from realistic motion sequences remains a challenge due to
pervasive and complex occlusions. Current methods struggle to capture the dynamics of
occluded body parts, leading to model penetration and distorted motion. RemoCap leverages
Spatial Disentanglement (SD) and Motion Disentanglement (MD) to overcome these limitations.
SD addresses occlusion interference between the target human body and surrounding objects.
It achieves this by disentangling target features along the dimension axis. By aligning
features based on their spatial positions in each dimension, SD isolates the target object's
response within a global window, enabling accurate capture despite occlusions. The MD module
employs a channel-wise temporal shuffling strategy to simulate diverse scene dynamics. This
process effectively disentangles motion features, allowing RemoCap to reconstruct occluded
parts with greater fidelity. Furthermore, this paper introduces a sequence velocity loss
that promotes temporal coherence. This loss constrains inter-frame velocity errors, ensuring
the predicted motion exhibits realistic consistency. Extensive comparisons with
state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on benchmark datasets demonstrate RemoCap's superior
performance in 3D human body reconstruction. On the 3DPW dataset, RemoCap surpasses all
competitors, achieving the best results in MPVPE (81.9), MPJPE (72.7), and PA-MPJPE (44.1)
metrics.